Sensors
Banner offers new and innovative technology in photoelectrics, laser distance measurement, ultrasonics, and fiber optics to solve almost any industrial automation application.
The Sensor Selection Guide briefly explains Banner’s array of sensing technologies, and helpful flowcharts make it easy to find the right sensor for any application.
-

-

Fiber Optic Amplifiers
-
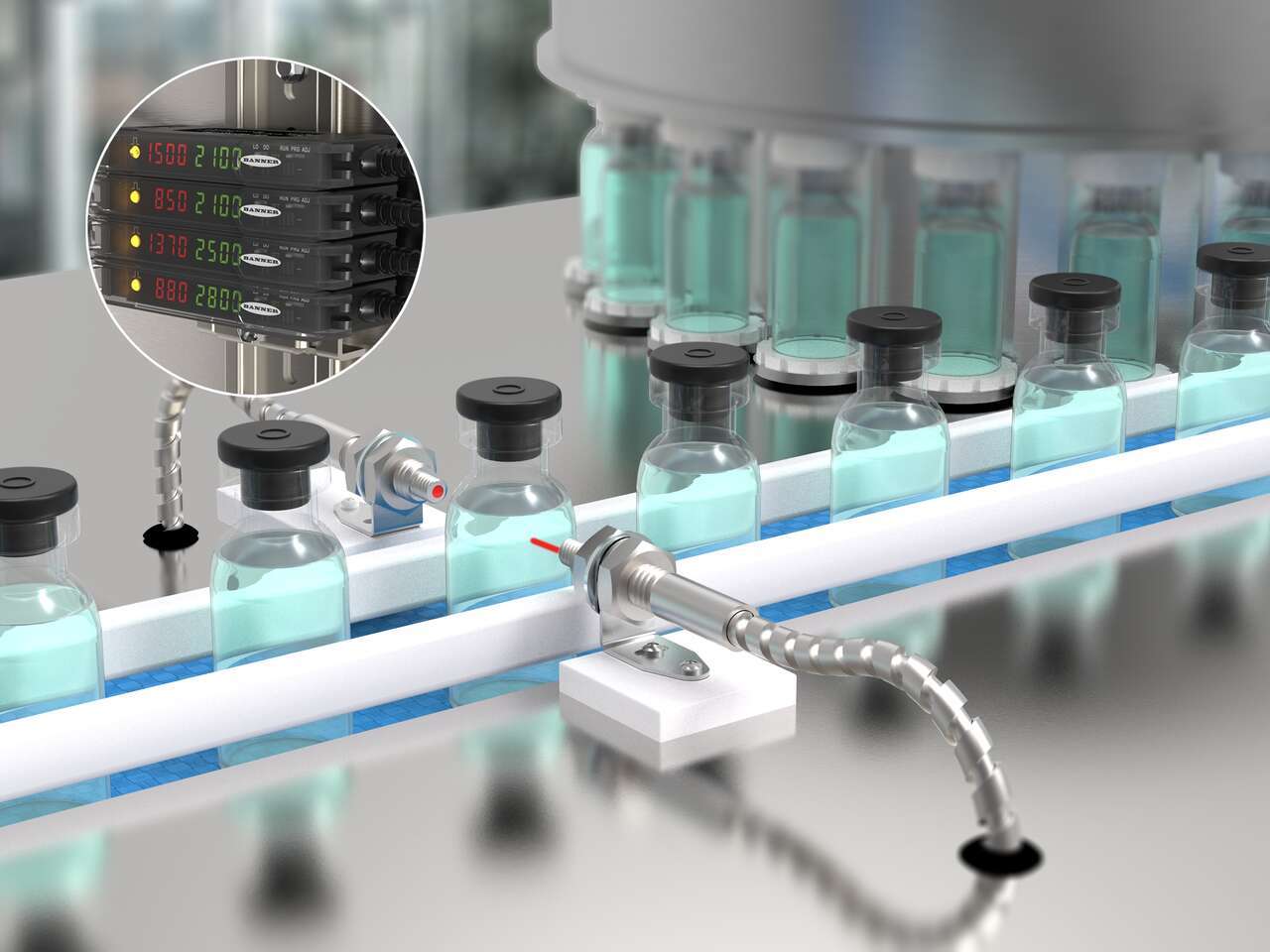
Fiber Optics
-

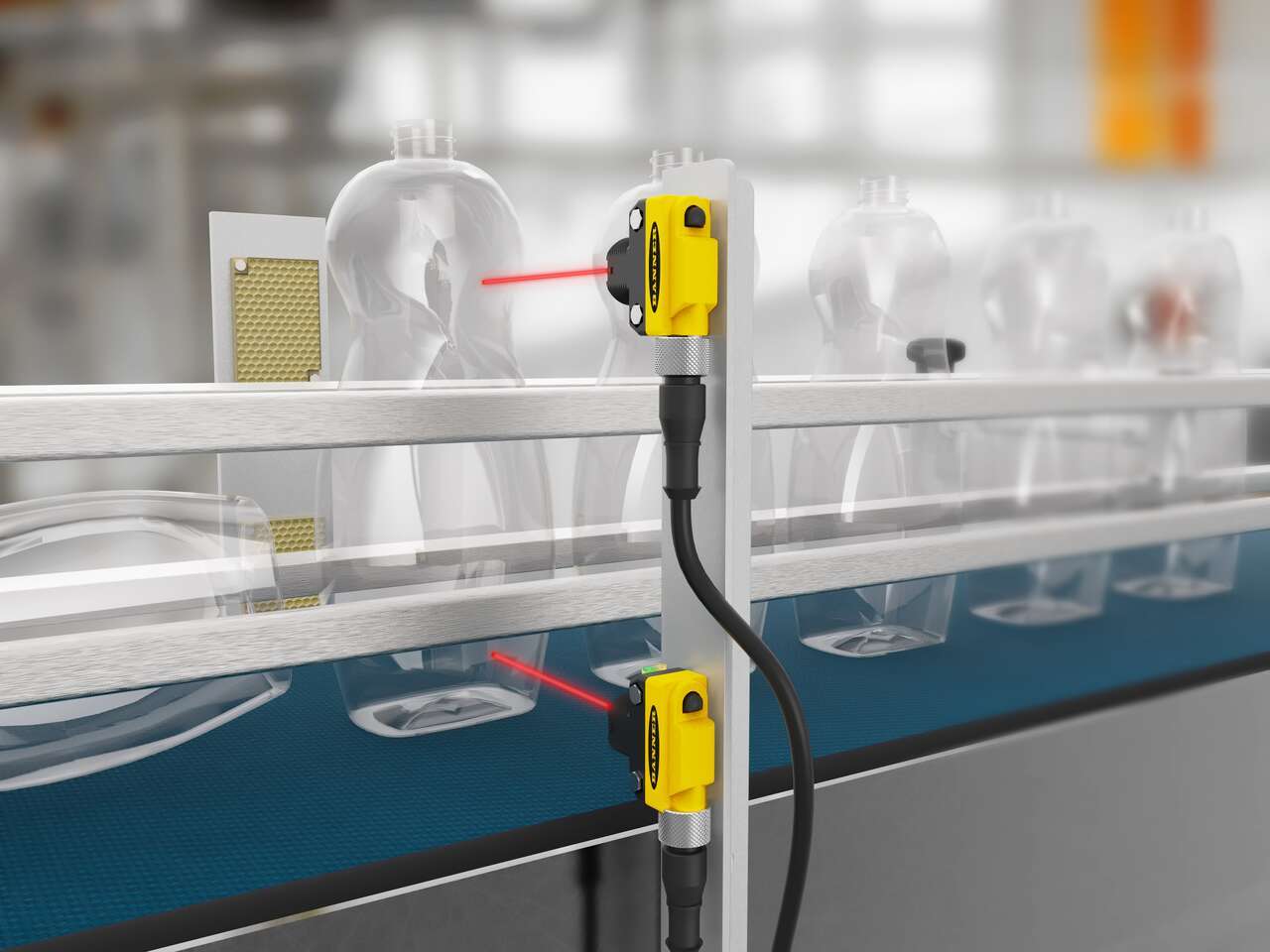
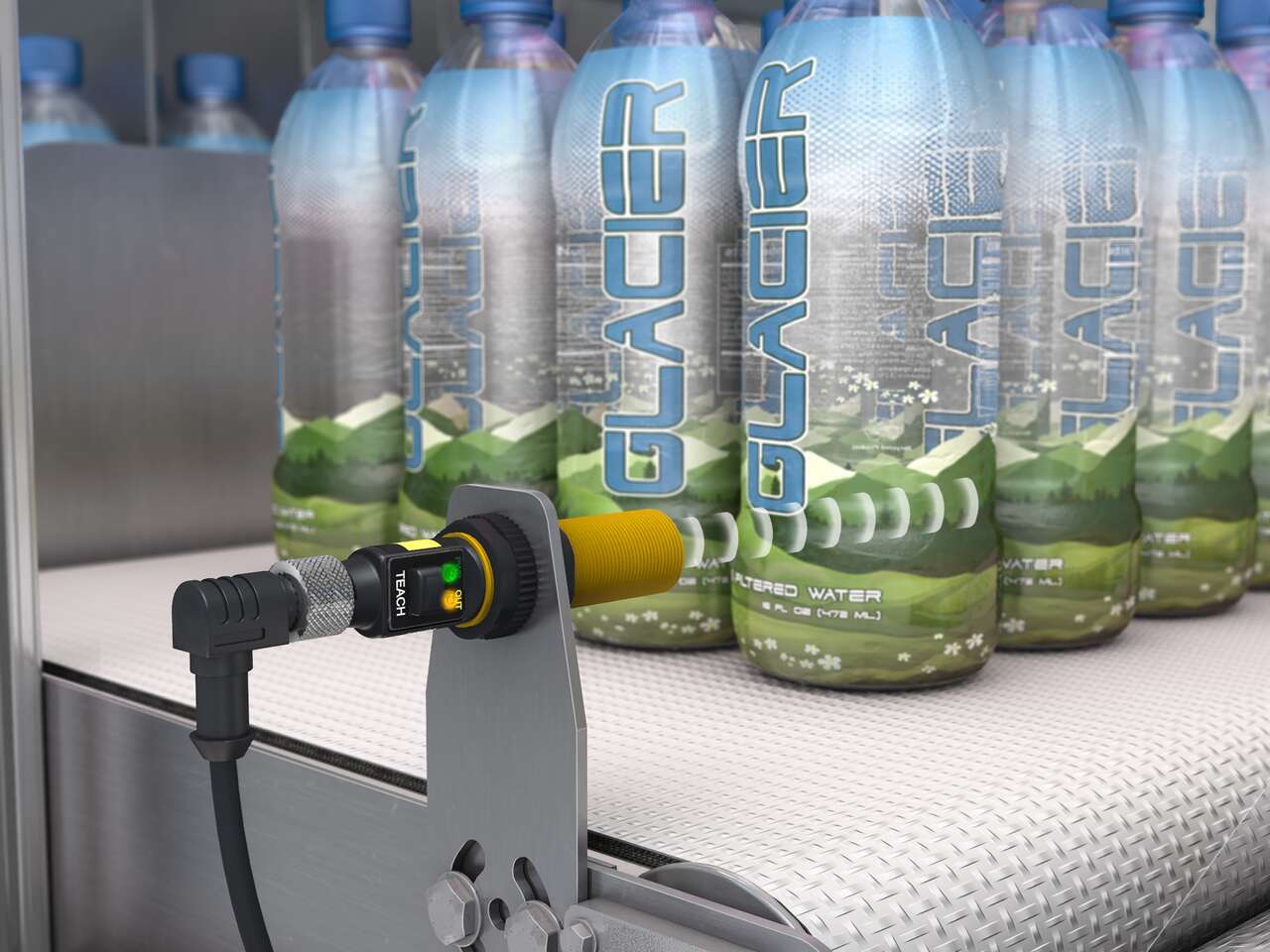
Slot, Label, Edge, and Area Detection Sensors
-
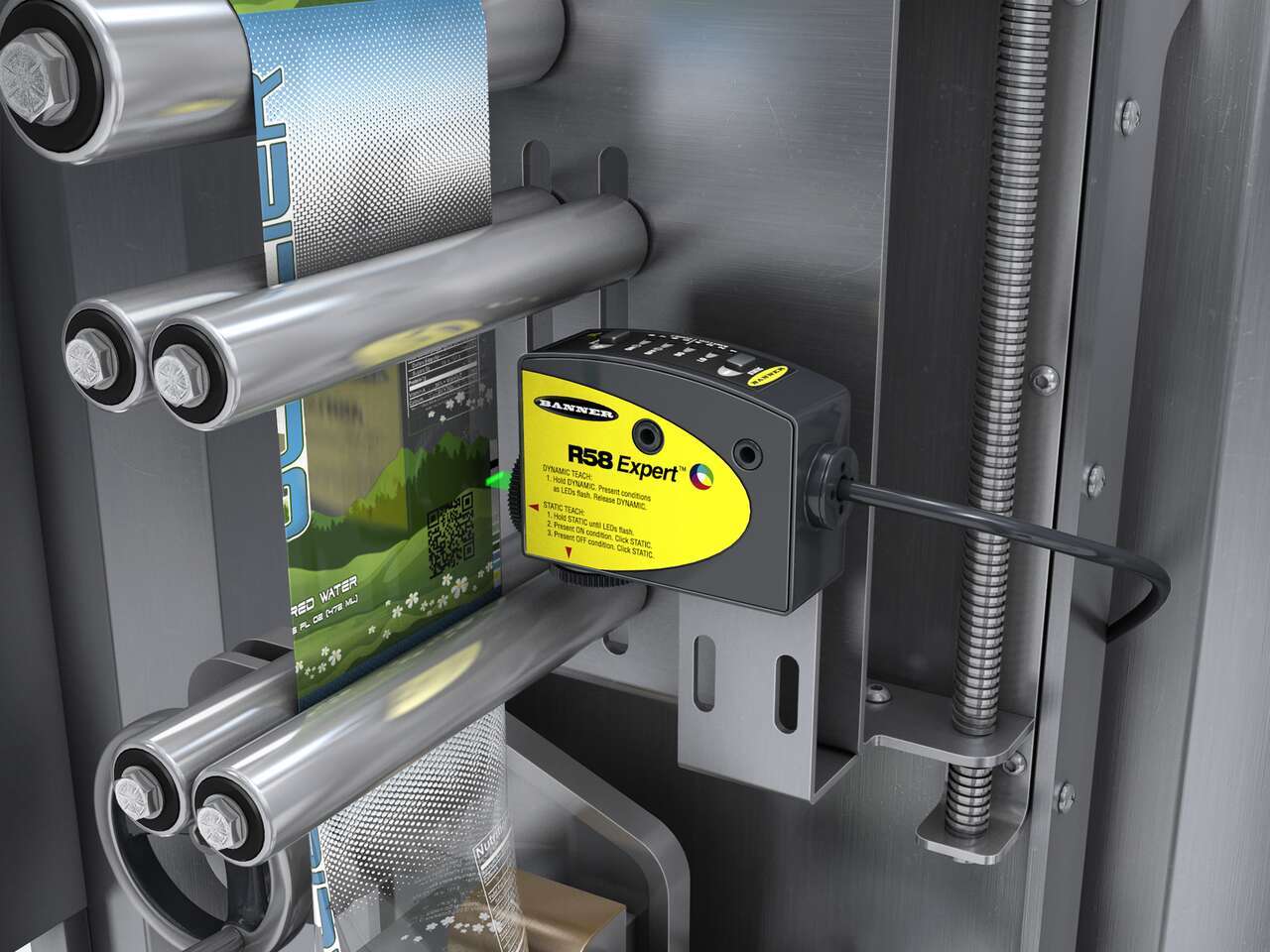

Registration Mark, Color and Luminescence Sensors
-

Sensor Software
-
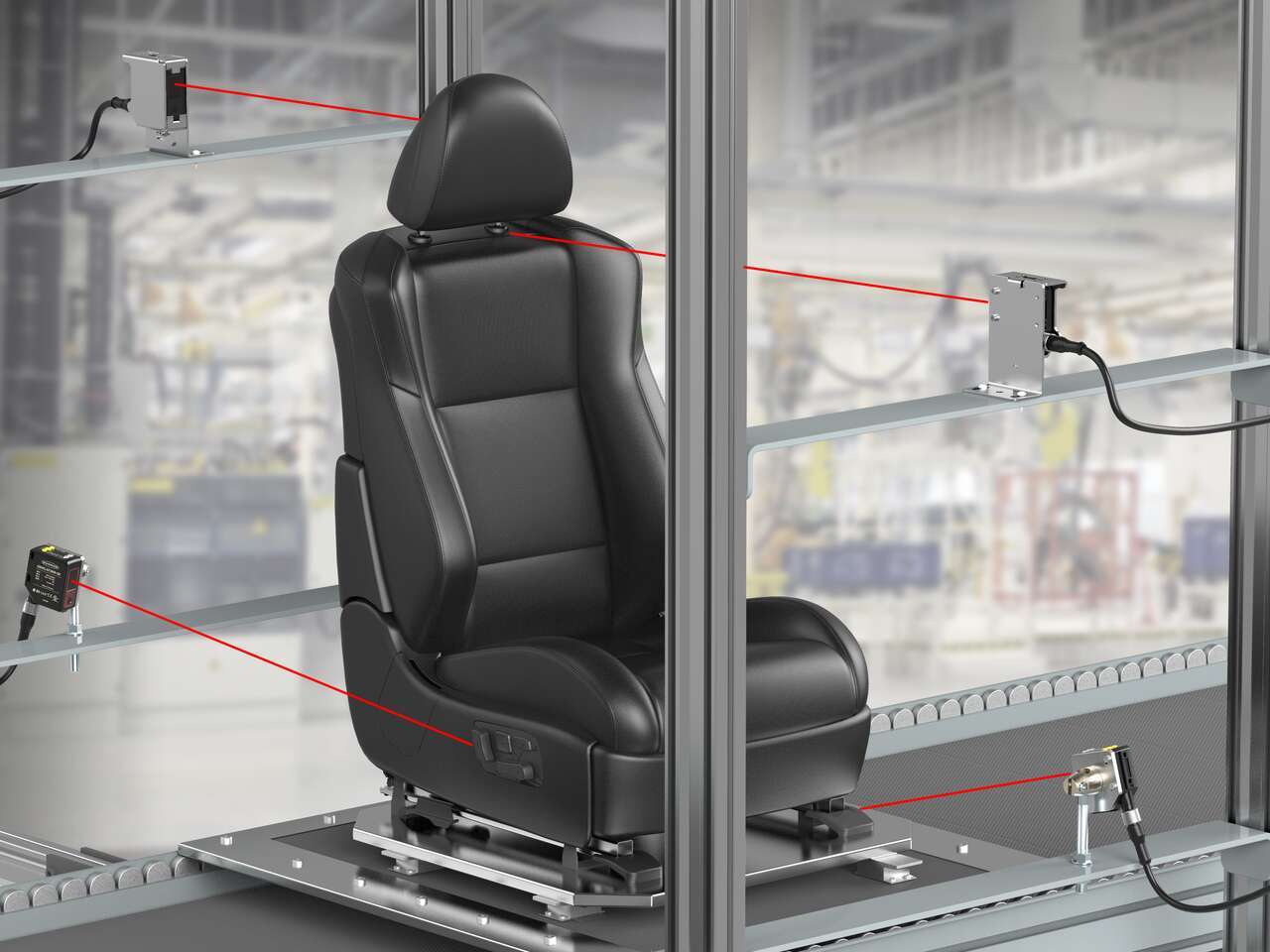

Laser Distance Measurement
-

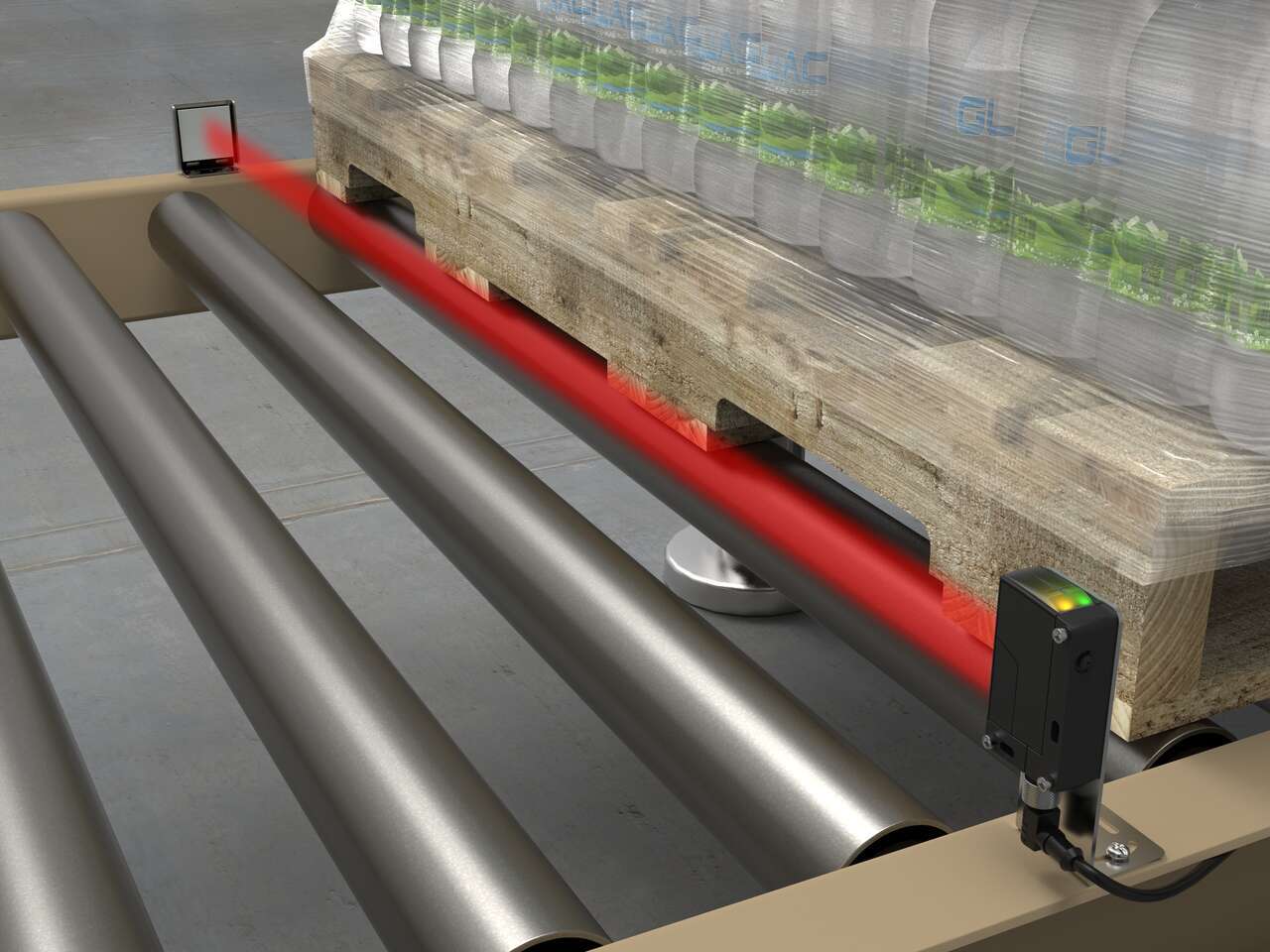
Radar Sensors
-

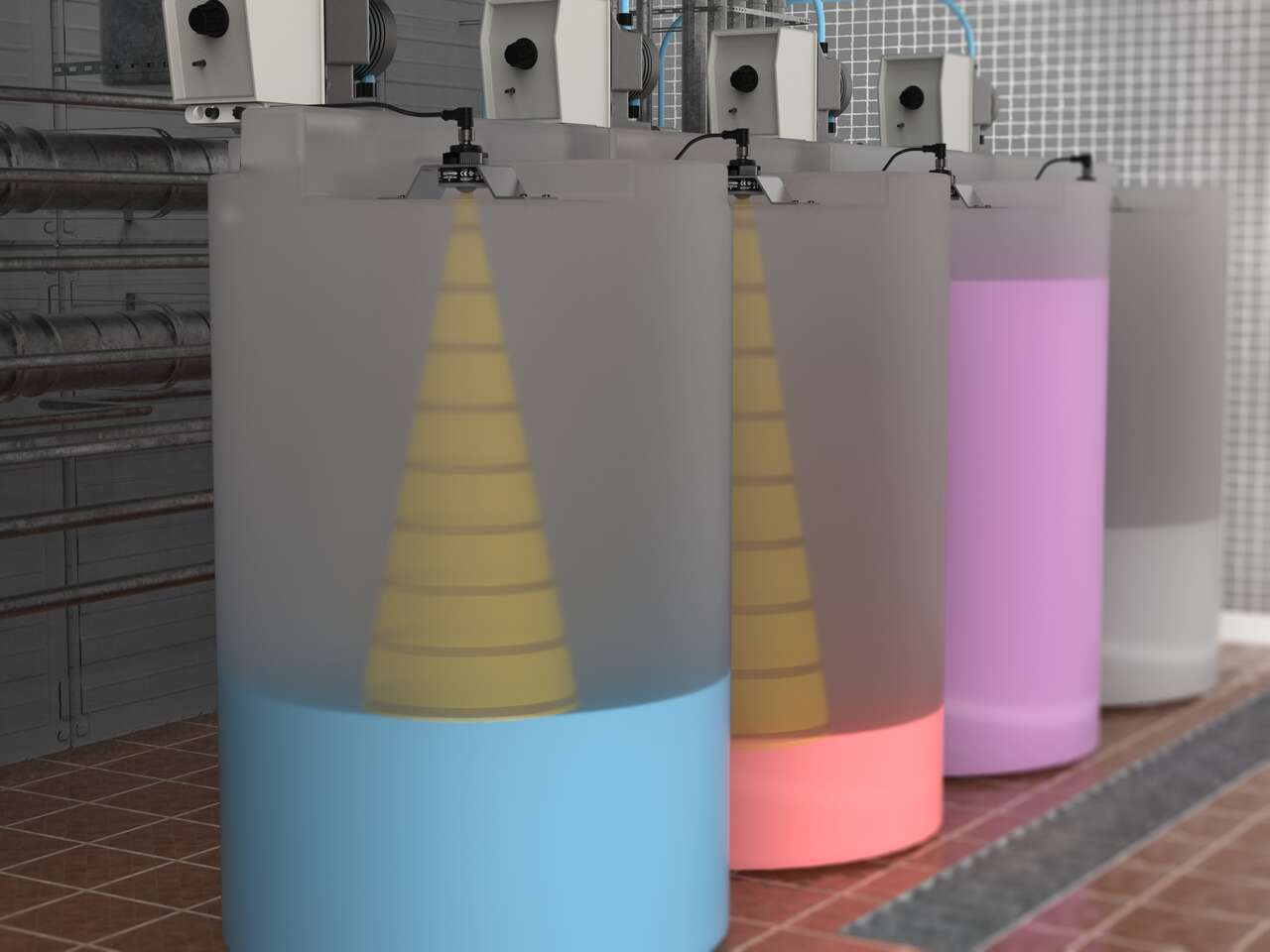
Ultrasonic Sensors
-
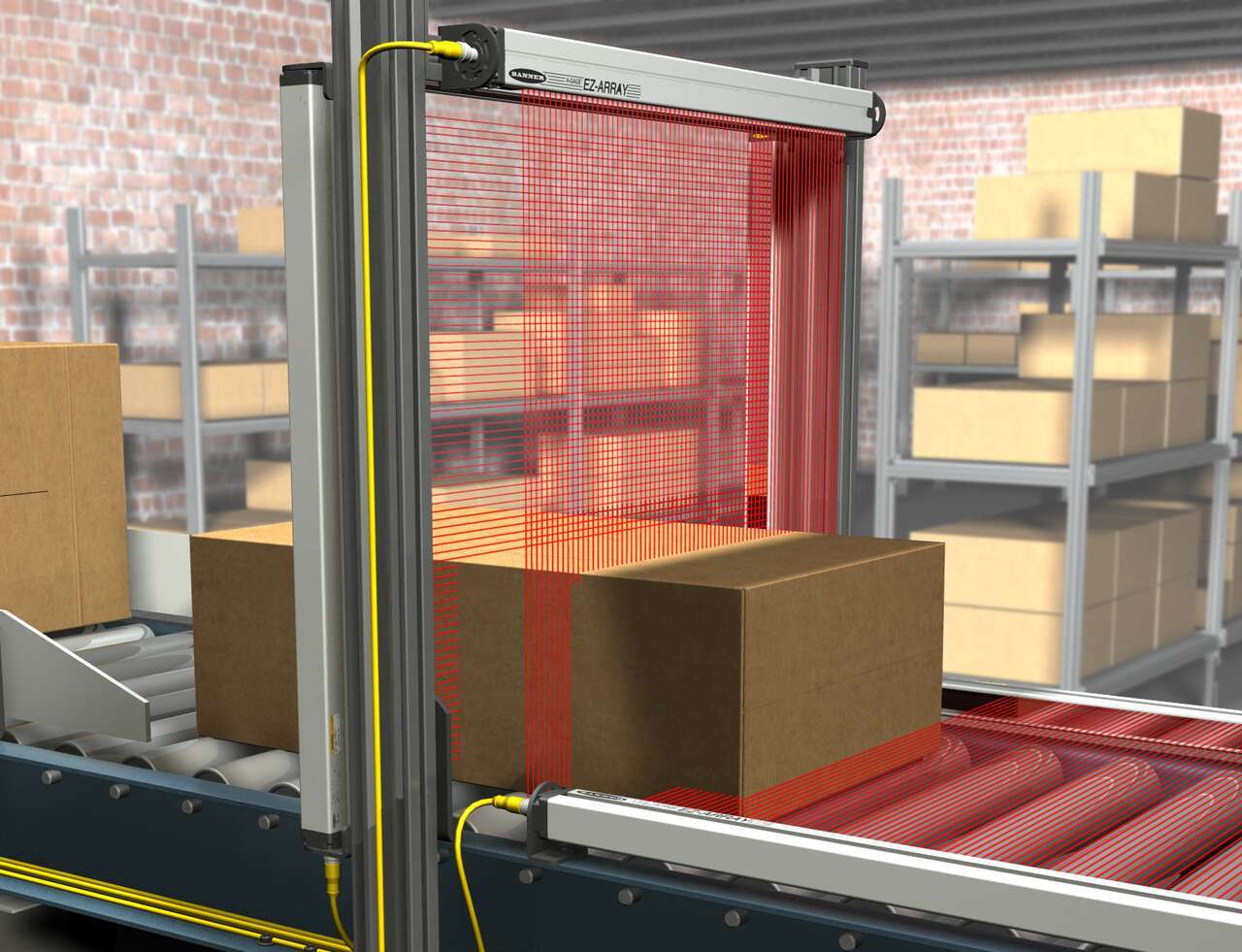

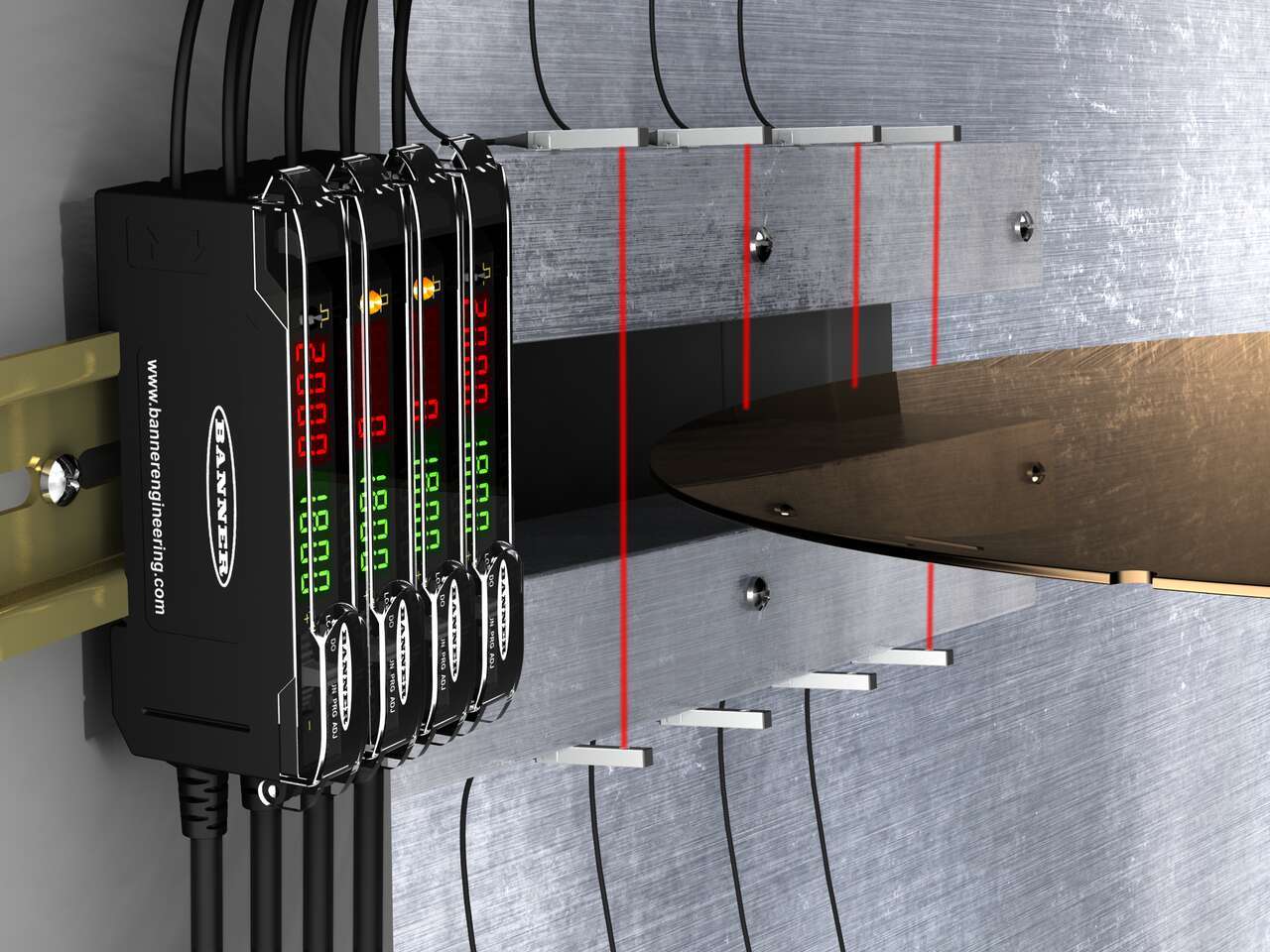
Measuring Arrays
-
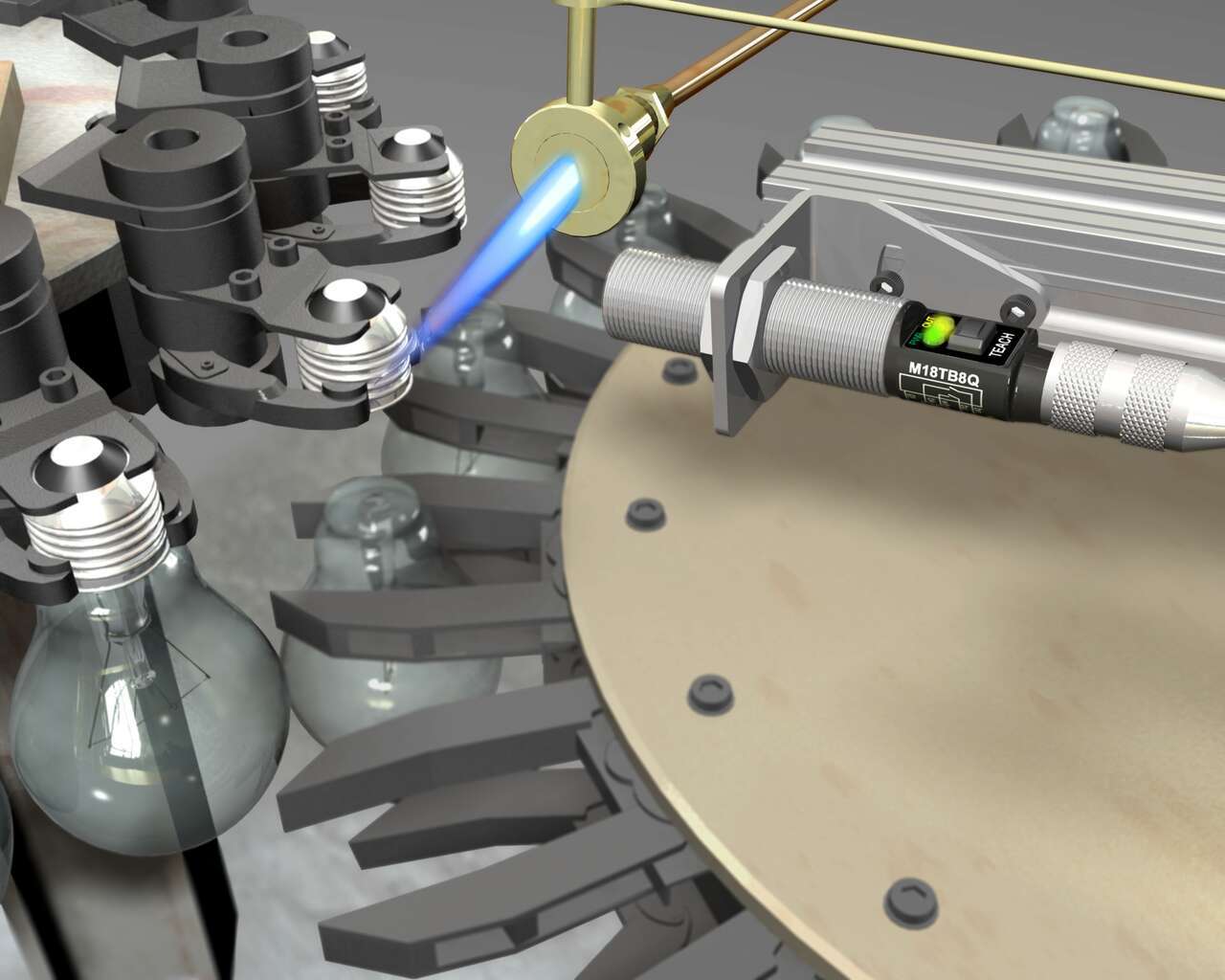
Temperature Sensors
-
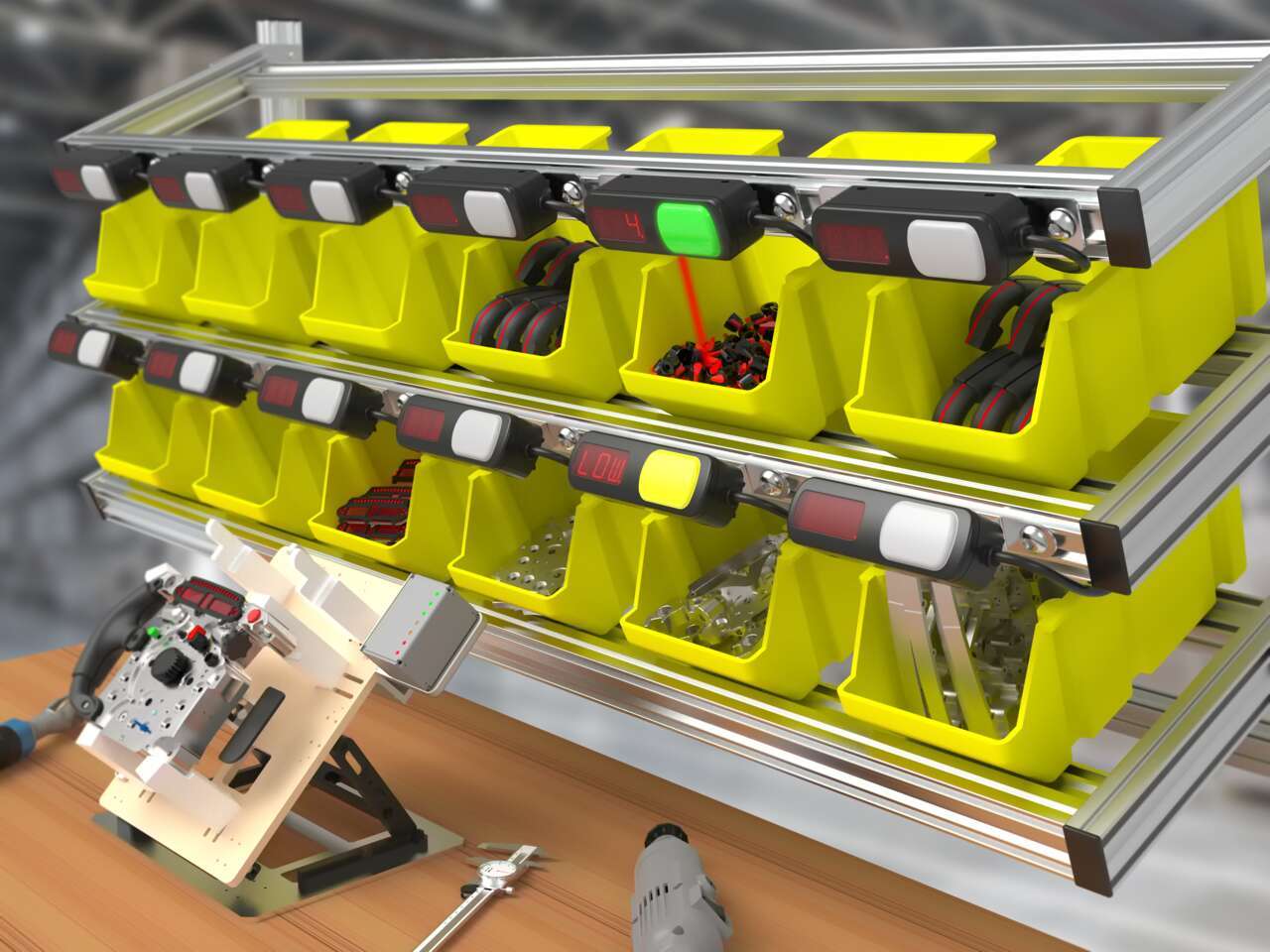
Pick-to-Light Sensors
-
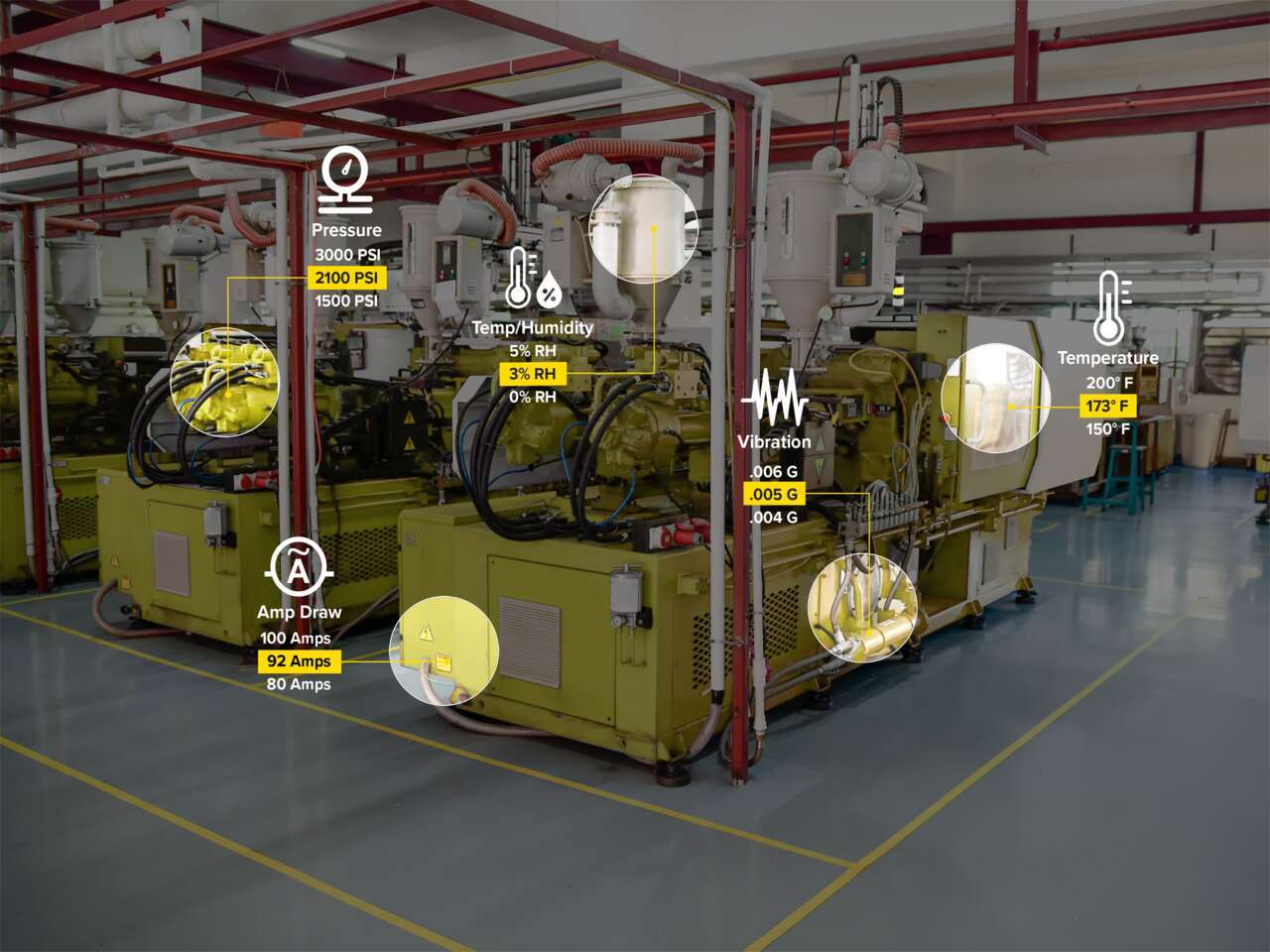

Condition Monitoring Sensors
-
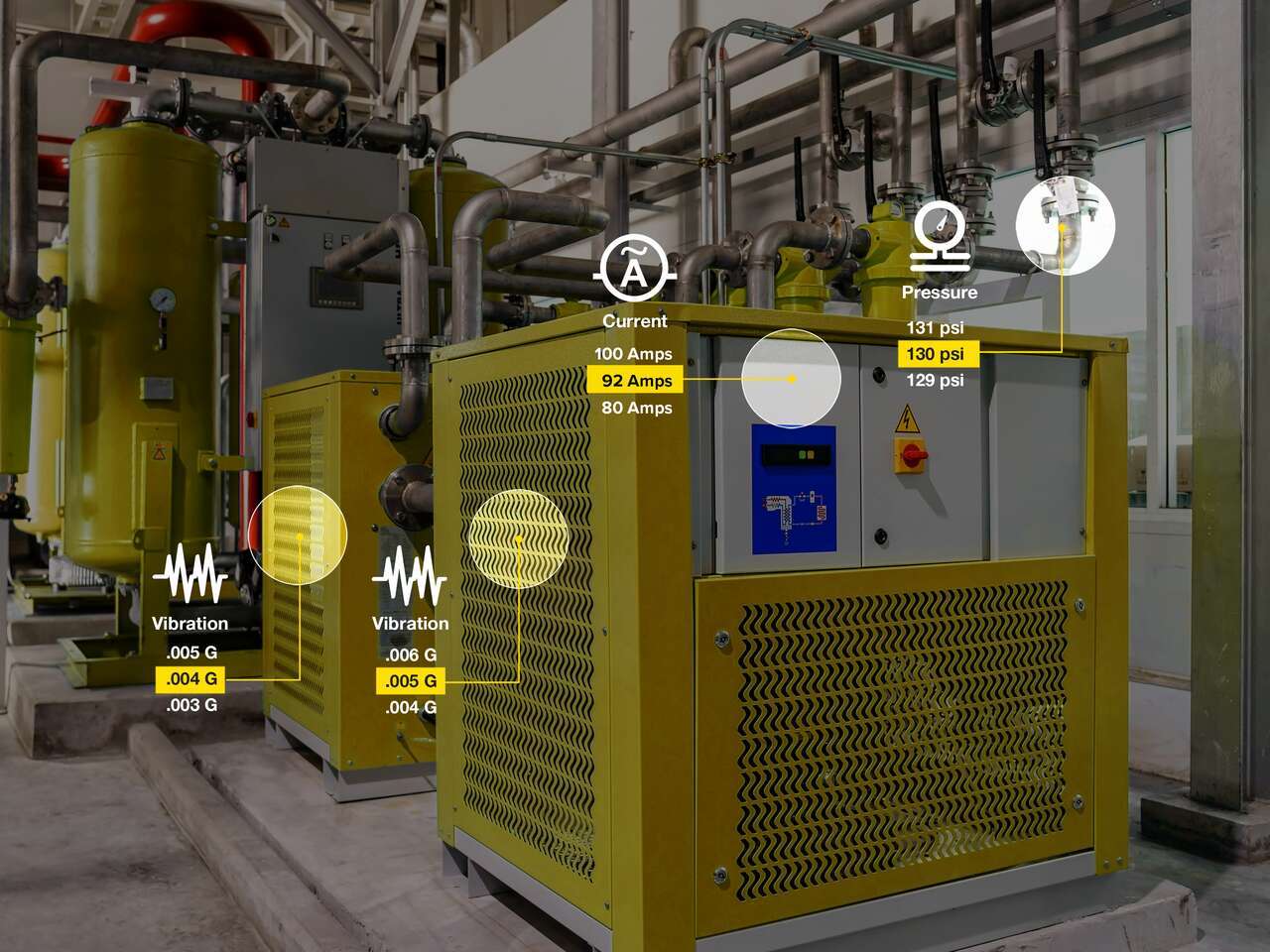

Wireless Condition Monitoring Sensors

-
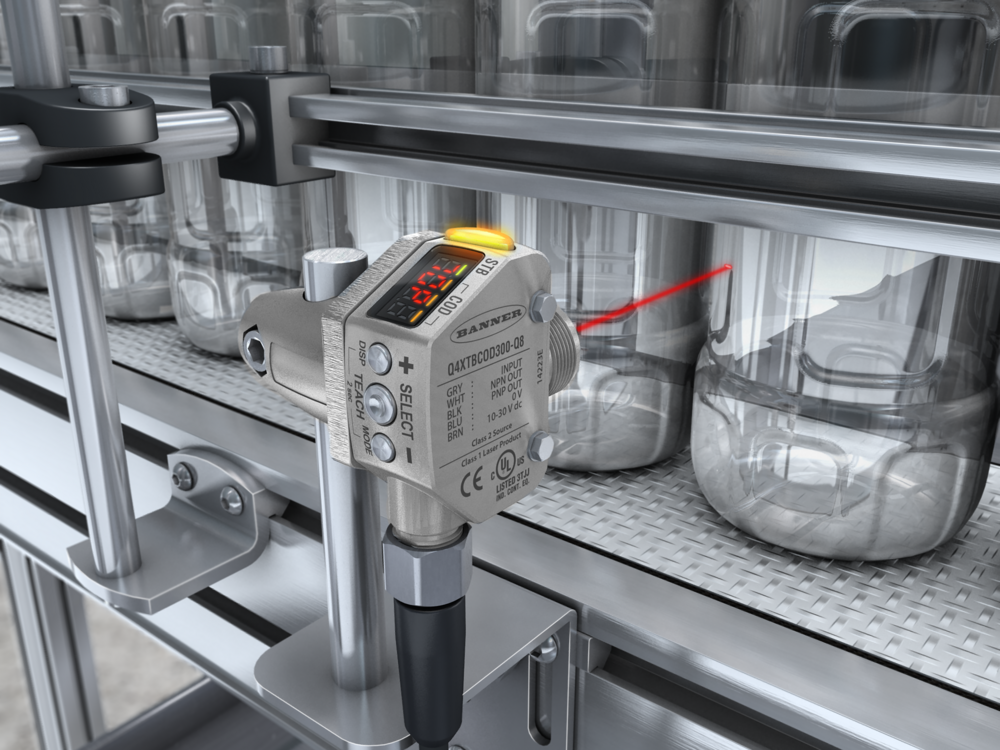

Laser Measurement Sensors with Dual Mode | Sensors
Detecting Clear and Reflective TargetsDetecting clear and reflective objects are some of the most challenging sensor applications. Light can burn through a target or be reflected away erratically, making accurate detection difficult.
-
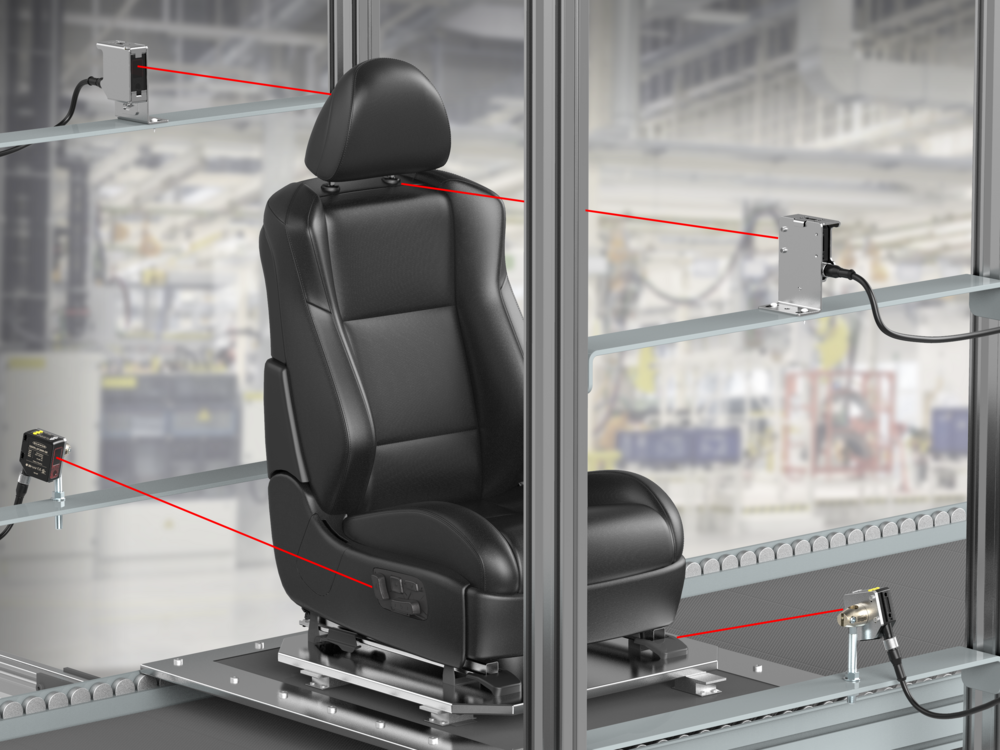

Verify Multiple Conditions with a Single Device | VS8
Complex ApplicationsDark objects are difficult to detect since they reflect very little light back to the sensor. In addition, black on black targets (low contrast between target and background) are especially challenging.
-

Make Better, Data-Driven Decisions
IO-Link CommunicationThis article describes how IO-Link provides users with remote monitoring capabilities for sensors and can help increase uptime, productivity, and throughput.
FAQs
What sensors are good in dusty environments?
Sensors with high excess gain are better at detecting targets in environments with elevated levels of airborne contaminants. Purge collars are accessories that prevent contaminants from collecting on the sensor face (not compatible with ultrasonic sensors). Excess gain for a sensor is found in the data sheet.
How does adjusting the potentiometer affect detection range?
A potentiometer increases or decreases the excess gain of the sensor. A higher excess gain has a stronger signal and can travel further.
How does vibration of machinery affect the sensing beam reaching its targets?
Vibrations can change the beam positioning. A larger beam spot is more forgiving when mounted on machinery over a smaller beam spot.
What is the best angle to point at a target?
It is best to pass a target normal to the sensor face, object motion should be perpendicular to the emitter and receiver.
What is the difference between light operate and dark operate wiring?
Light operate triggers the output when the receiver receives the sensing beam, dark operate triggers the output when the receiver does not receive the sensing beam. Depending on the specific sensor wiring, this can correspond to normally open and closed wiring.
What is the relationship between accuracy/resolution/precision and distance?
Increasing the range between the sensor and the target lowers the accuracy of the reading. If you need high precision, it is better to look for a short-range sensor.
In general, what do the indicators on the sensor mean?
- The steady green indicator is on when power is being supplied to the sensor.
- The steady amber indicator is on when the receiver is seeing more than enough light intensity from the emitter, a high excess gain.
- The flashing amber indicator is on when the receiver is seeing enough light from the emitter, but it is near the threshold of required excess gain.
- The green indicator is off when power supplied to the sensor is insufficient.
- The amber indicator is off when the receiver is not seeing any light from the emitter, or the light intensity is not above the required excess gain.
Does the sensor retain its memory (taught conditions) after power cycling?
Most sensors have non-volatile memory so they can store their taught conditions even when the power supply is interrupted.