Drive Thru Vehicle Detection and Monitoring
Improve Customer Experience and Maximize Profits
Drive thru applications require reliable vehicle detection to alert employees to a customer’s presence at a window, count the number of cars passing through, monitor time spent in the drive thru, and more.
By increasing efficiency and facilitating a better customer experiece, vehicle detection solutions not only save costs but also maximize revenue.
Inductive loops have traditionally been a common vehicle detection technology for drive thru applications. However, inductive loop systems require large sections of pavement or brickwork to be damaged and removed for installation and repairs, which can lead to lengthy downtime.
Radar is another technology that can be used for drive thru vehicle detection. Radar sensors are immune to weather conditions, making it an excellent option for outdoor deployments at drive thru businesses.
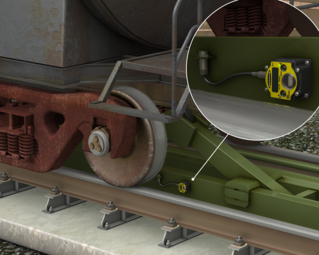
Wireless magnetometers are an excellent choice when wired technology is impractical. Wireless magnetometers can be installed above or below grade, and even below grade installations are minimally invasive, requiring only a small 3-inch diameter hole in the concrete for each sensor location.
Keep reading to learn how these technologies solve common drive thru vehicle detection challenges; or contact an engineer to discuss your specific application.


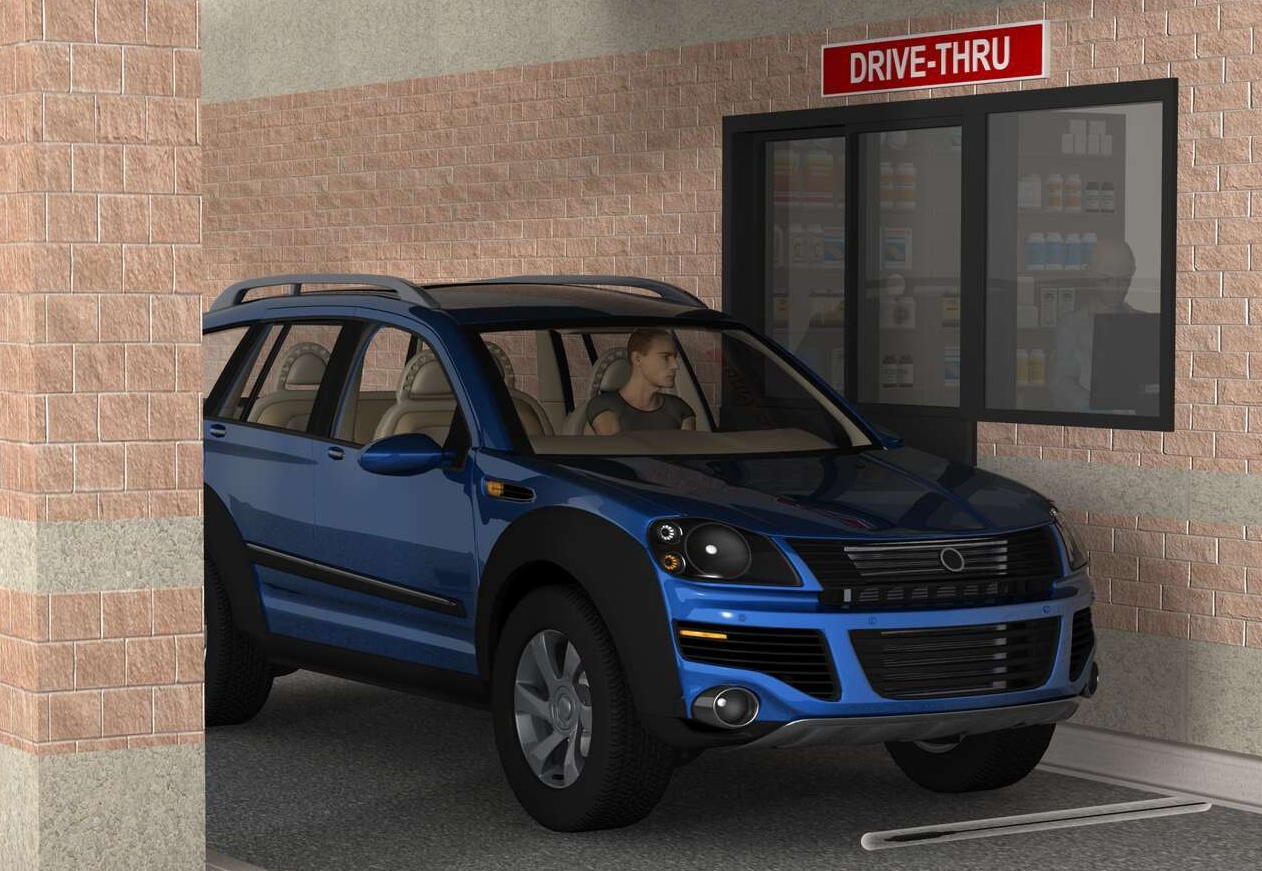
Vehicle Detection at a Quick Serve Restaurant
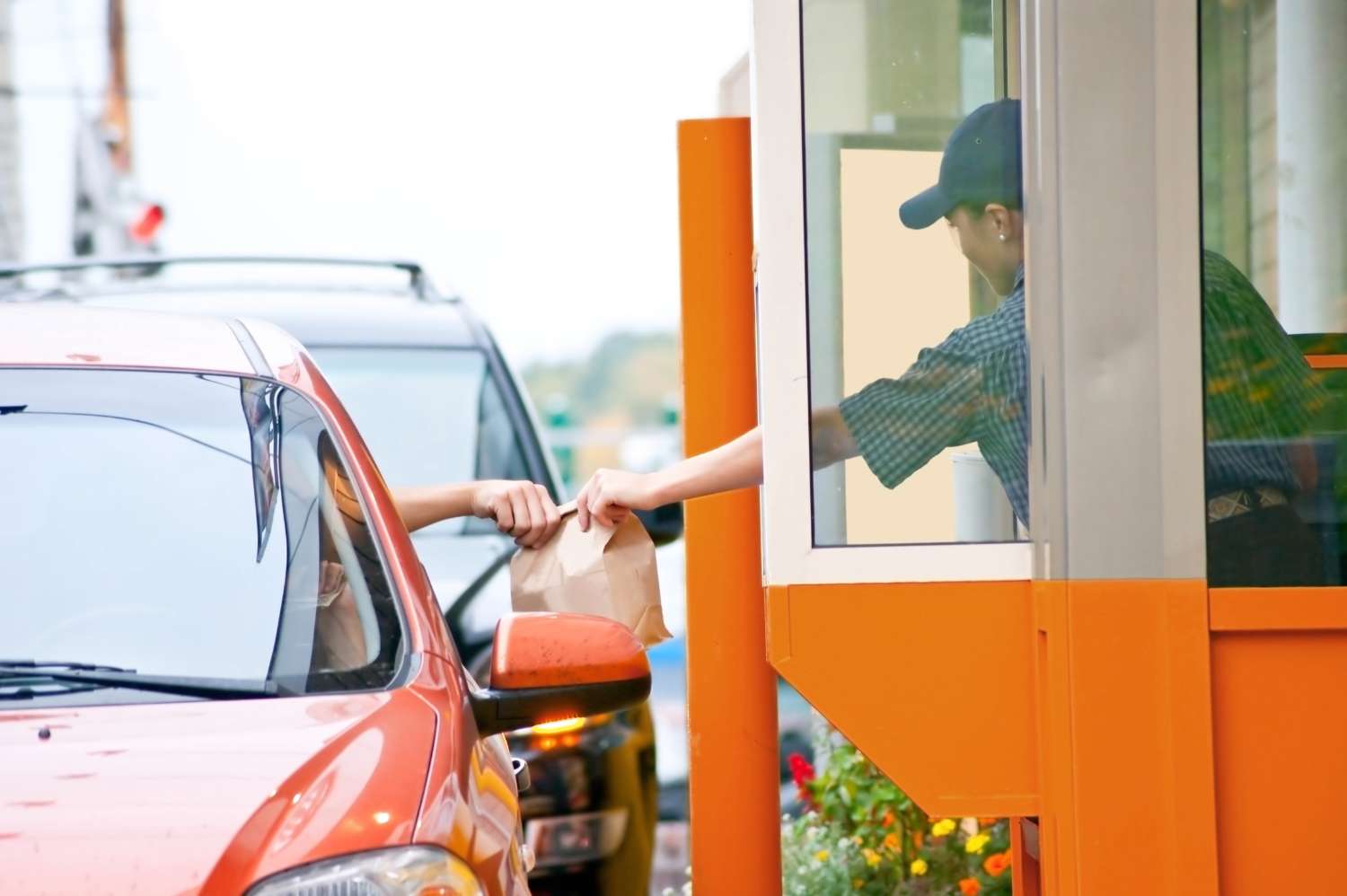
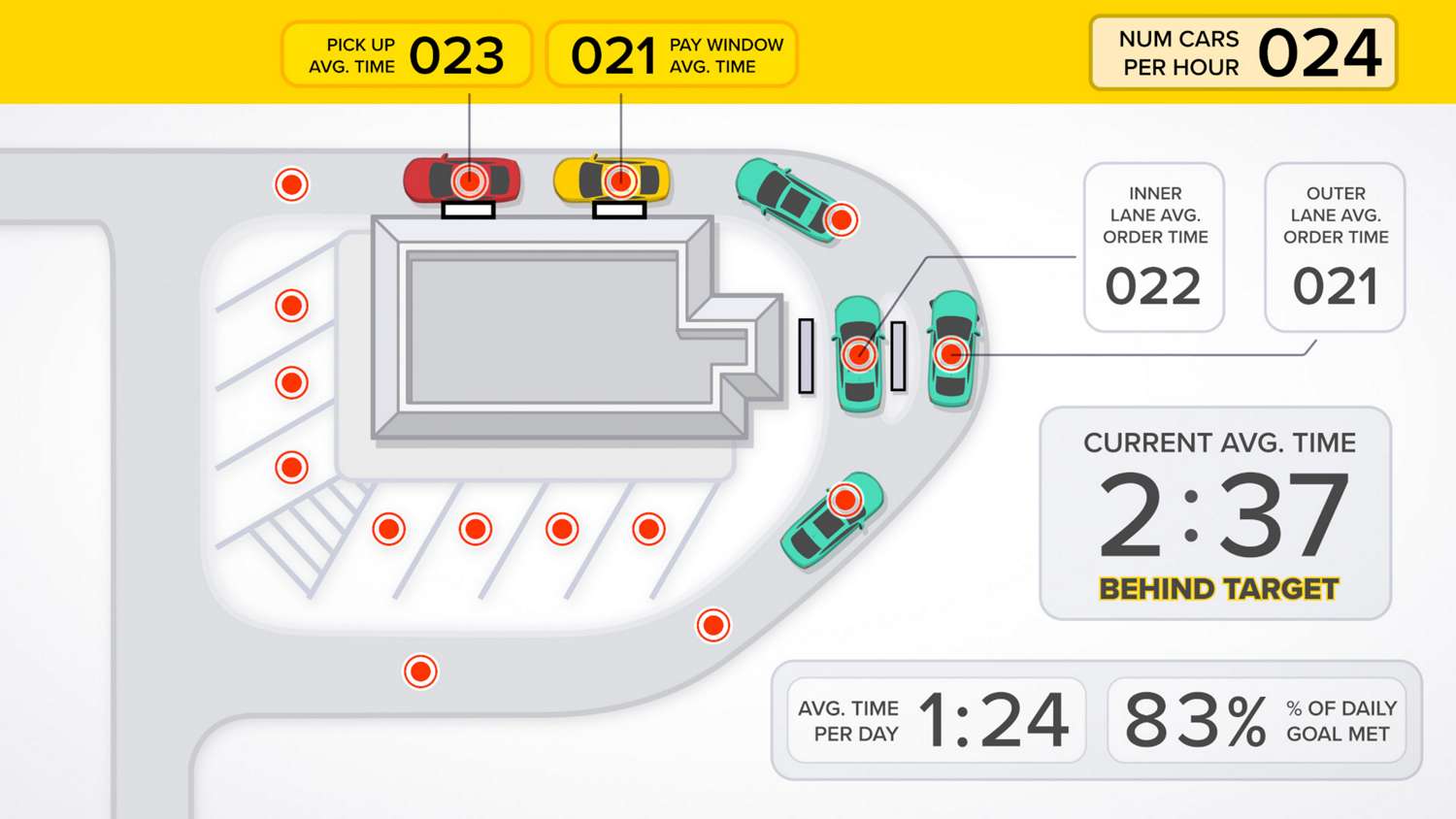
Fast food restaurants rely heavily on their drive-thru service, and they earn much of their revenue from drive-thru sales. Streamlining the drive-thru process in quick serve restaurants (QSR) can increase revenue and improve customer satisfaction.
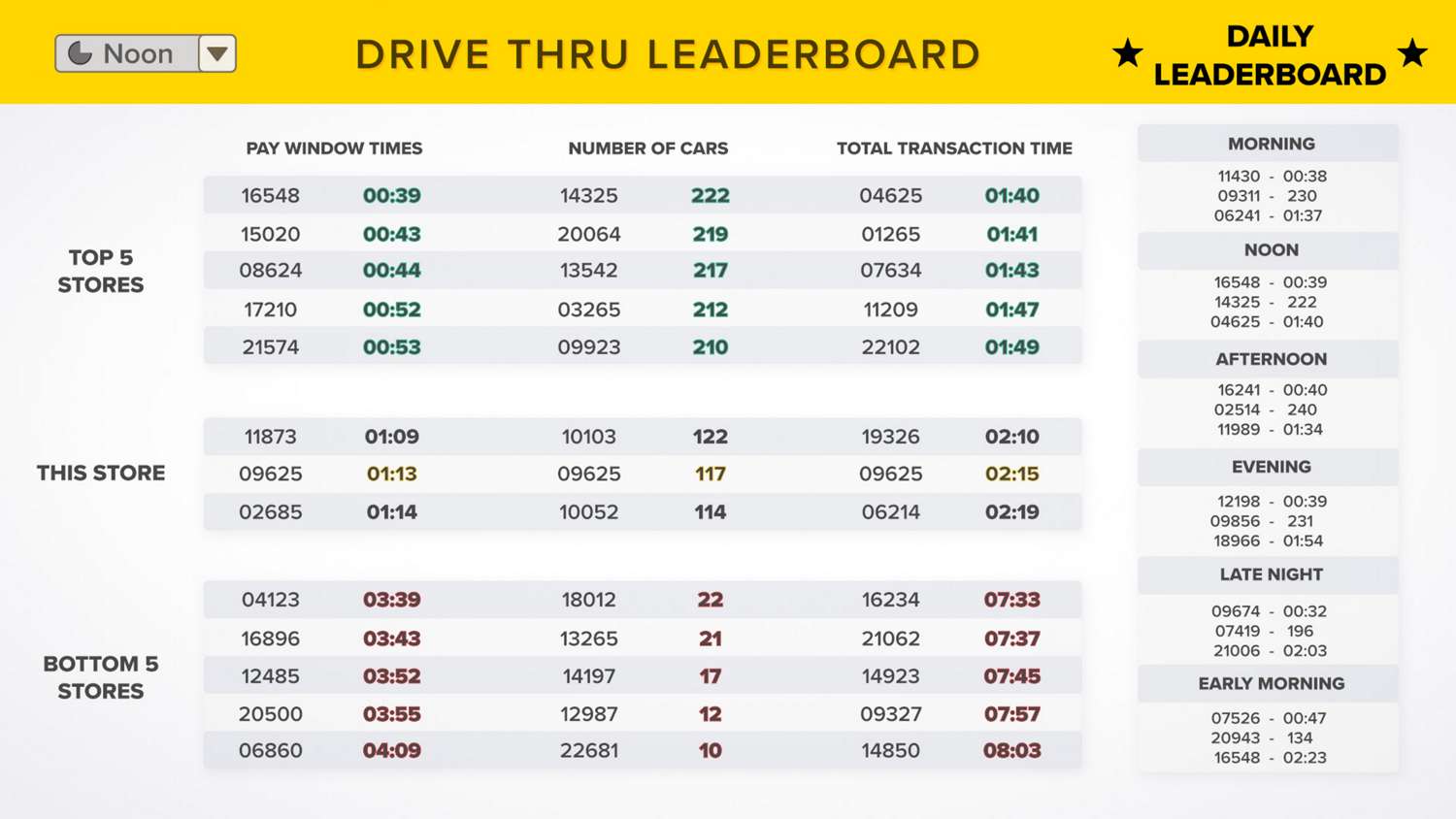
By combining wireless vehicle detection sensors with an analytical software platform, restaurants can track the speed of service and compare drive-thru times at multiple locations. This visibility enables managers to identify where bottlenecks occur, and it allows stores to compete to improve their drive-thru service.
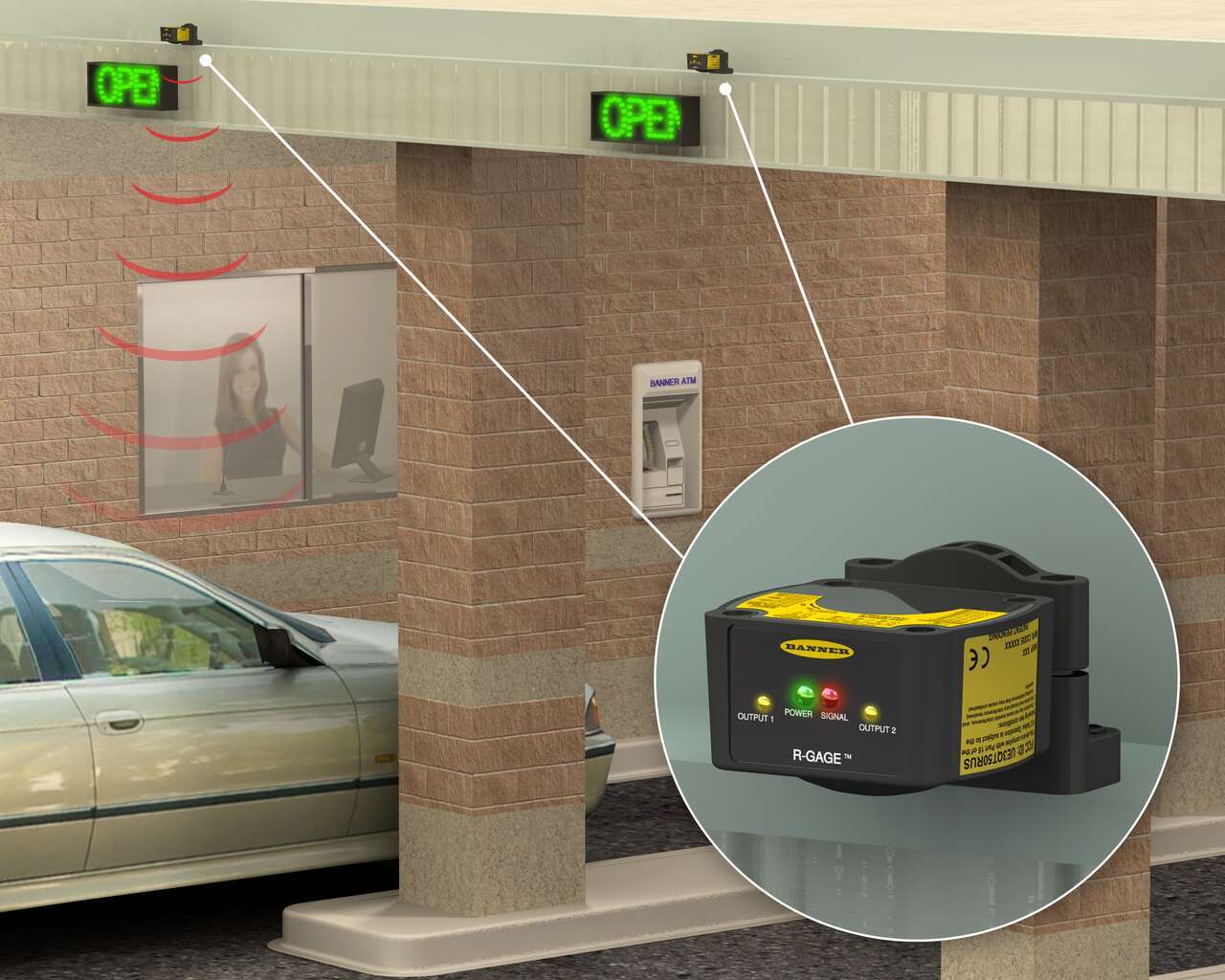
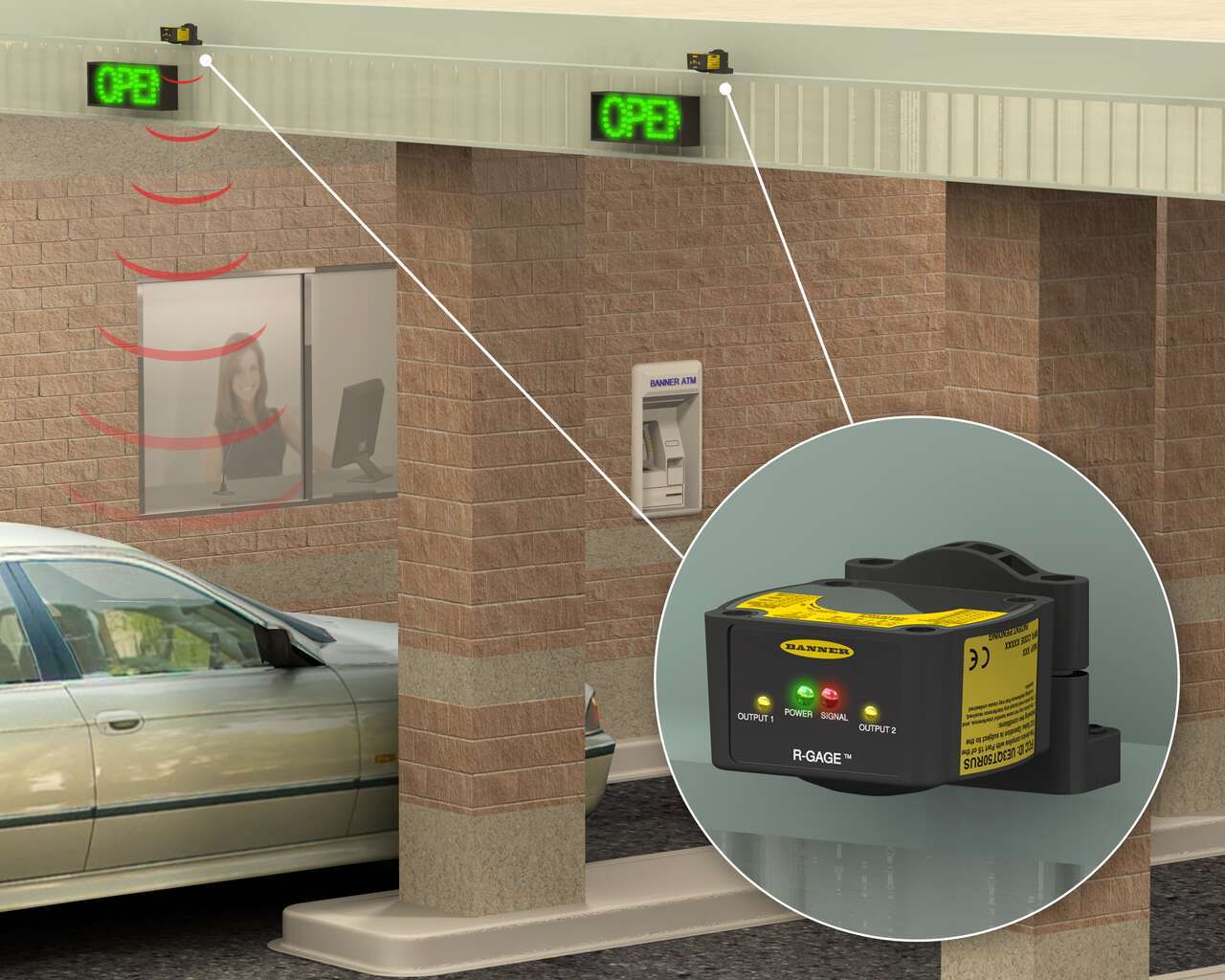
Vehicle Detection at a Bank Drive Thru
In applications where staff may be away from the drive thru window for periods of time, a vehicle detection solution can be used to alert staff when a customer is present. For example, bank tellers working the drive-up windows must be aware when a vehicle is present in order to optimize customer service.
Radar sensors use Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave Radar (FMCW) to detect both stationary and moving vehicles. In the application pictured to the right, a radar sensor is mounted to the drive-through overhang and is configured to detect the pavement.
When a vehicle blocks the beam, the sensor’s output switches and a signal is sent to the bank workers, alerting them of the presence of the vehicle to ensure timely service and minimal wait times for customers.
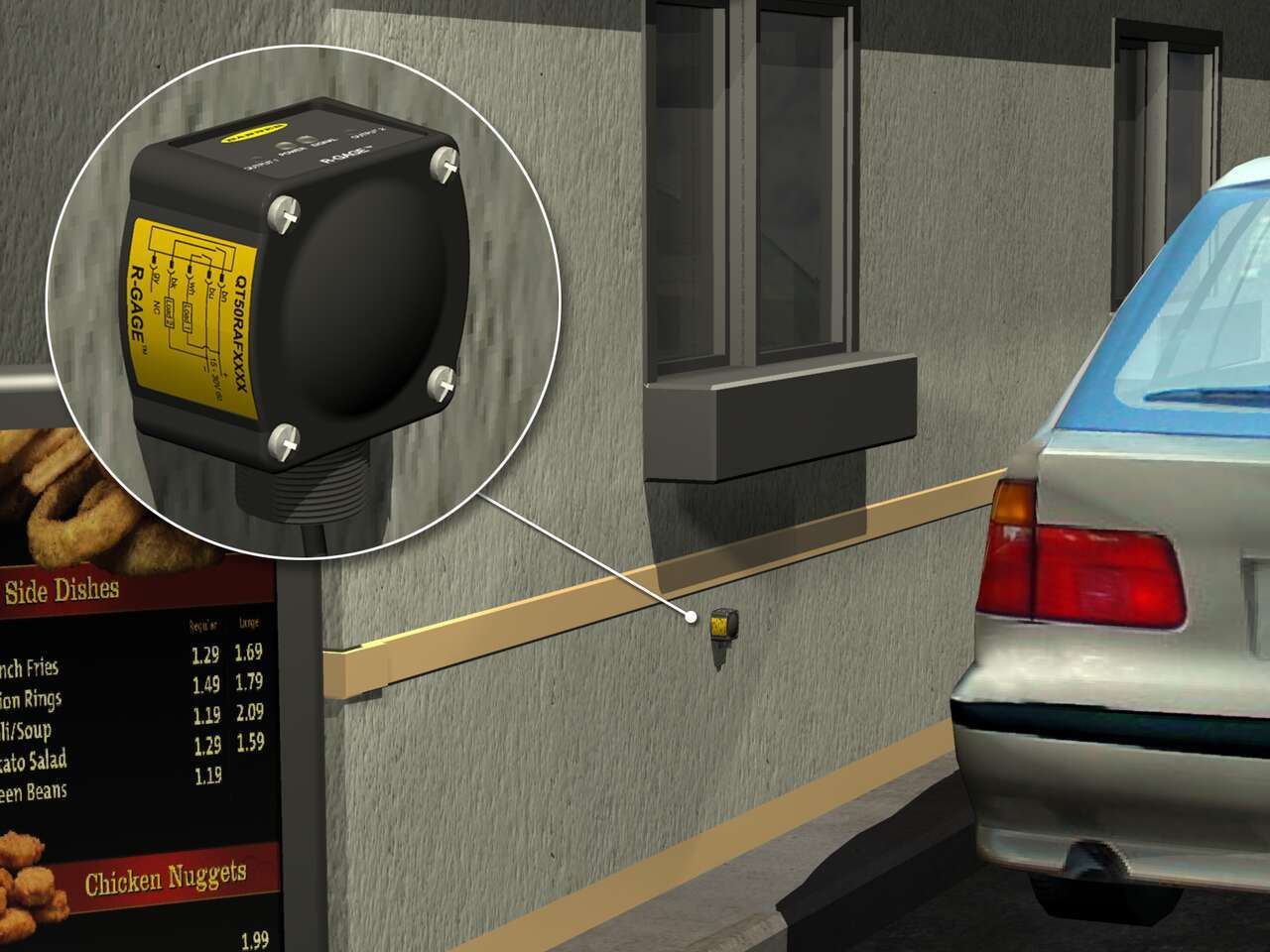
Vehicle Detection and Counting at a Drive Thru
In addition to triggering a signal that a customer is present, radar sensors can also be used to count the number of vehicles that pass through the drive thru each day. This provides valuable information on peak drive thru days and times to facilitate data-driven staffing decisions.
The radar sensor's vehicle detection, business indication, and count functions help restaurants efficiently respond to drive-thru customers, measure drive-thru demand, and manage drive-thru operations.
Wireless Magnetometers for Vehicle Detection
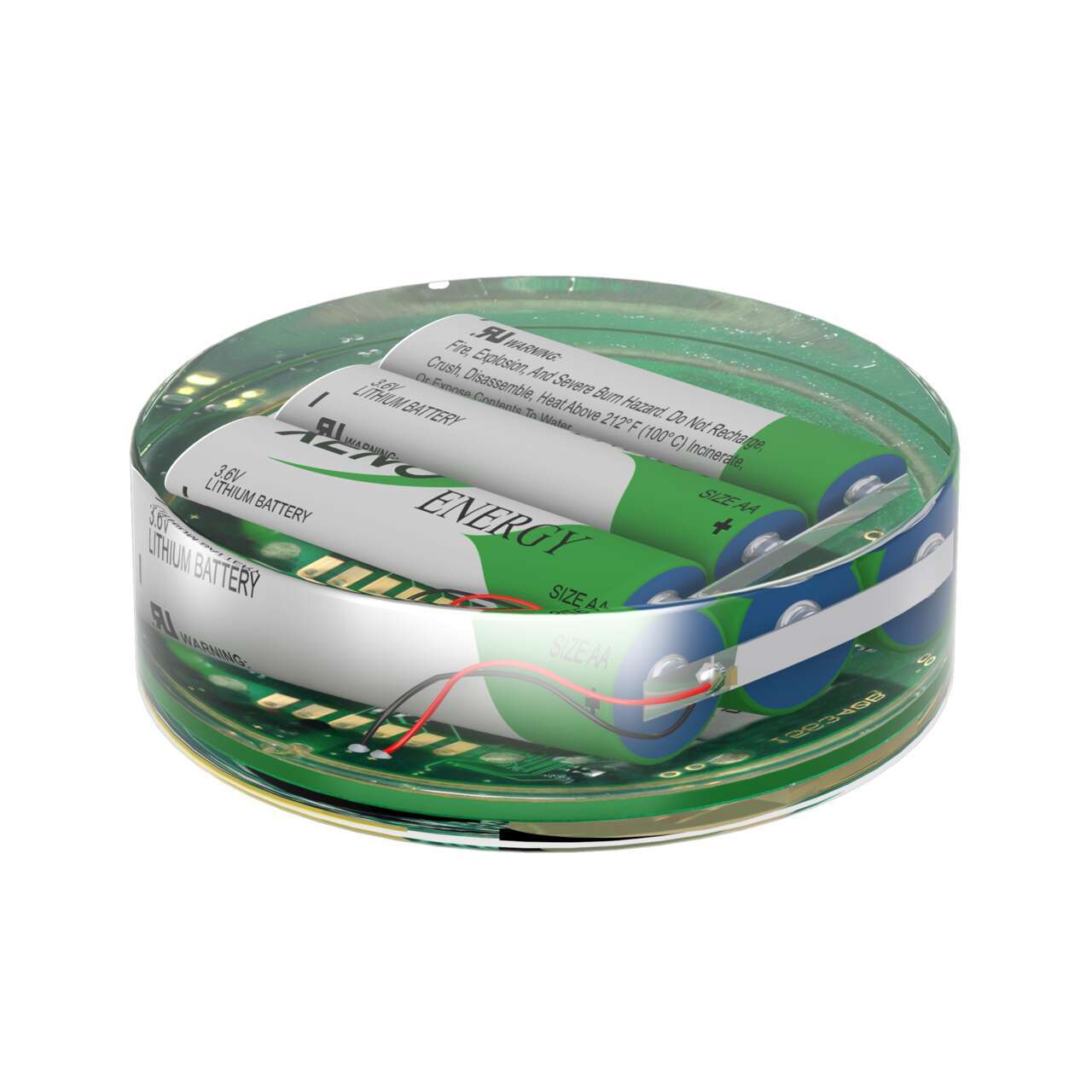
The M-GAGE sensor uses passive sensing technology to detect large ferrous objects, such as motor vehicles. The M-GAGE provides an alternative replacement for inductive loop systems and needs no external control box.
- Designed to minimize the effects of temperature change and fluctuating magnetic fields
- Sensor learns ambient background and stores settings in non-volatile memory
- FlexPower technology driven by a single, primary lithium battery integrated into the housing
- Transceivers provide two-way communication between the Gateway and Node, including fully acknowledged data transmission
- Fully potted and sealed housing contains the power source, sensor, and antenna for a completely wireless solution
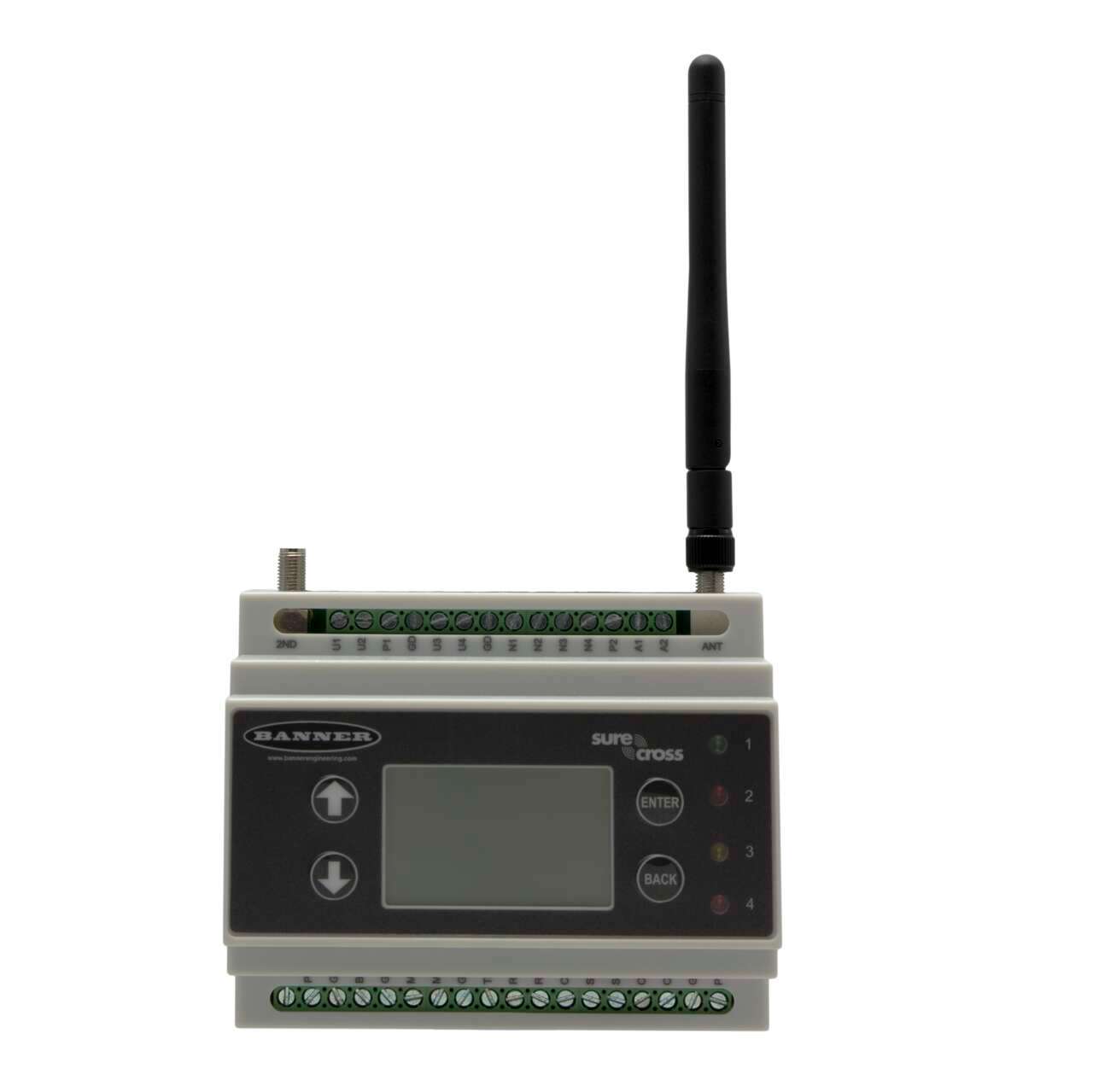
Wireless Controller
DXM Series industrial wireless controllers are designed to facilitate Ethernet connectivity and Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) applications.
- ISM radios available in 900 MHz and 2.4 GHz for local wireless network
- Converts Modbus RTU to Modbus TCP/IP or Ethernet I/P
- Logic controller can be programmed using action rules and text language methods
- Micro SD card for data logging
- Email and text alerts
- Cell modem for cellular connectivity
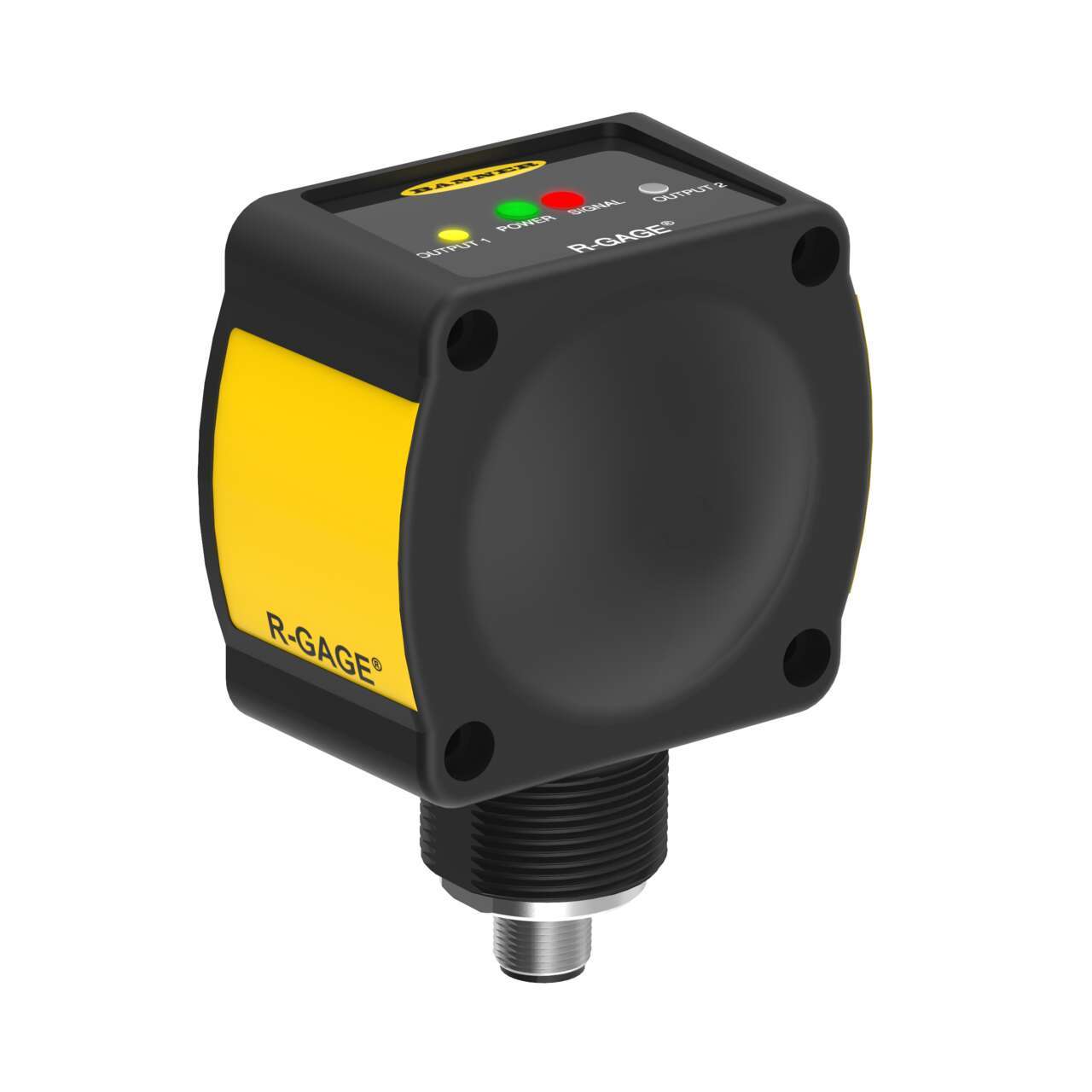
Radar Sensor
High sensitivity radar-based sensors ideal for collision avoidance on board mobile equipment, like reach stackers, forklifts, and mining vehicles.
- Fourth generation FMCW (true-presence) radar detects moving and stationary objects
- Higher sensitivity and longer range
- Adjustable sensing field — ignores objects beyond setpoint
- Easy setup and configuration of range, sensitivity, and output with simple DIP switches
- Sensing functions are unaffected by wind, falling rain or snow, fog, humidity, air temperatures, or light
- Sensor operates in Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM) telecommunication band no special license required
- Rugged IP67 housing withstands harsh environments